CVPR 2023 Tutorial:
Denoising Diffusion Models:
A Generative Learning Big Bang
Location: West 202-204.
Format: Hybrid (registration needed).
Virtual link location: [link (registration needed)]
Recording: See blow.

Links to tutorial slides: [Part 1: Fundamentals] [Part 2: Images] [Part 3: Others]
Recording is now available [here].
Overview
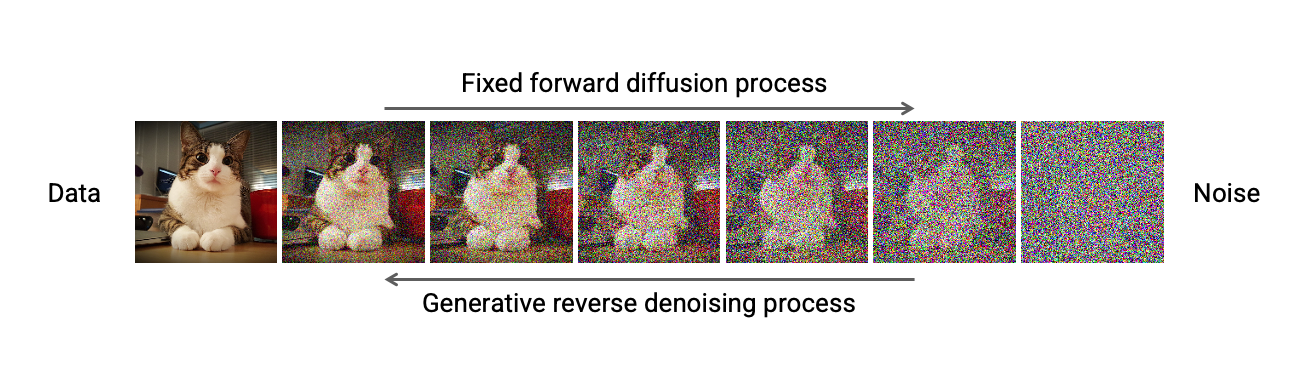
Score-based denoising diffusion models (diffusion models) have been successfully used in various applications such as text-to-image generation, natural language generation, audio synthesis, motion generation, and time series modeling. The rate of progress on diffusion models is astonishing. In the year 2022 alone, diffusion models have been applied to many large-scale text-to-image foundation models, such as DALL-E 2, Imagen, Stable Diffusion and eDiff-I. These developments have also driven novel computer vision applications, such as solving inverse problems, semantic image editing, few-shot textual inversion, prompt-to-prompt editing, and lifting 2d models for 3d generation. Diffusion models have been widely adopted in various computer vision applications and are becoming a dominating class of generative models. This popularity is also reflected in the diffusion models tutorial in CVPR 2022, which has accumulated nearly 60,000 views on YouTube over 8 months.
Despite that, there has been tremendous novel work on diffusion models since last year, a lot of which we believe are critical for computer vision practitioners. The following are just a few notable examples: Eludicated Diffusion Models (NeurIPS 2022 best paper) provide principles on how one should train diffusion models in an optimal manner. Recent differential equation solvers such as DPM-Solver (NeurIPS 2022 Oral) and DEIS have made notable advances on accelerating sampling from diffusion models. Diffusion inversion techniques such as DreamFusion and Magic3d obtain text-to-3D generation by inverting image diffusion models. Textual inversion and DreamBooth enable the ``personalization'' of text-to-image diffusion models from few-shot supervision signals. There are also numerous recent works that apply diffusion models to other domains, such as 3d representations, videos, and motions. Given the rate of progress, we believe that it is crucial to have a tutorial on diffusion models in CVPR 2023, focusing on more recent developments.
The primary goal of this tutorial is to make diffusion models more accessible to a wider computer vision audience and introduce recent developments in diffusion models. Unlike the previous tutorial, we will streamline the discussion on fundamentals and focus much more on practical methods and applications of diffusion models. We will present successful practices on training and sampling from diffusion models and discuss novel applications that are enabled by diffusion models in the computer vision domain. These discussions will also heavily lean on recent research developments that are released in 2022 and 2023. We hope that this second tutorial on diffusion models will attract more computer vision practitioners interested in this topic to make further progress in this exciting area.
Speakers
Schedule
| Title | Speaker | Time (PST) |
|---|---|---|
| Fundamentals Training, sampling, guidance |
Arash Vahdat | 09:00 - 10:00 |
| Applications on natural images Architecture, editing, personalization, fine-tuning, "low-level" vision etc. |
Chenlin Meng | 10:15 - 11:15 |
| Applications on other domains Inverse problems, video, 3d, motion, large content generation, etc. |
Jiaming Song | 11:30 - 12:30 |
About Us
Jiaming Song is a research scientist at NVIDIA Research. Prior to joining NVIDIA, he worked on deep generative modeling at Stanford University, under the supervision of Stefano Ermon. He is the creator of DDIM, the earliest accelerated algorithm for diffusion models that is widely used in recent generative AI systems including DALL-E 2, Imagen, Stable Diffusion, and ERNIE-ViLG 2.0. He also served a critical role in developing SDEdit, which is used in Stable Diffusion for image-to-image translation. He also co-developed eDiff-I, NVIDIA's first large-scale text-to-image diffusion model. Jiaming is a recipient of the ICLR 2022 Outstanding Paper Award.
Chenlin is a CS PhD at Stanford University advised by Stefano Ermon. She was previously an intern at Google Brain working with Tim Salimans and Jonathan Ho. Her research interests include score-based generative models, diffusion models, variational autoencoders, autoregressive models, normalizing flows and other types of large-scale generative models. Specifically, she is interested in making large-scale generative models fast, controllable and scalable in real-world settings.
Arash Vahdat is a senior research manager at NVIDIA Research where he leads the generative AI team. Before NVIDIA, he was a researcher at D-Wave Systems, working on generative learning and its applications in label-efficient training. Before D-Wave, Arash was a research faculty member at Simon Fraser University, where he led computer vision research and taught master courses on machine learning for big data. Arash’s current research areas include generative learning, representation learning, and efficient learning.